
UX Research Tools: Which to Use and When
Customer person
This is a way to model the target audience of the created product. There can be several persons if the product involves several market segments or roles within the product. For example, a teacher's person for an LMS and a student's person for a front-end product in the EdTech industry. Images should describe the expectations and motivations of future users.
How to form images (persons)?
- From observing people in the real world.
- From patterns based on responses in study groups.
- From narrowly focused projects (for example, an application for people with anxiety disorders).
- Focus only on the main features: goals, expectations, motives, and not archetypes, age, stereotyped properties.

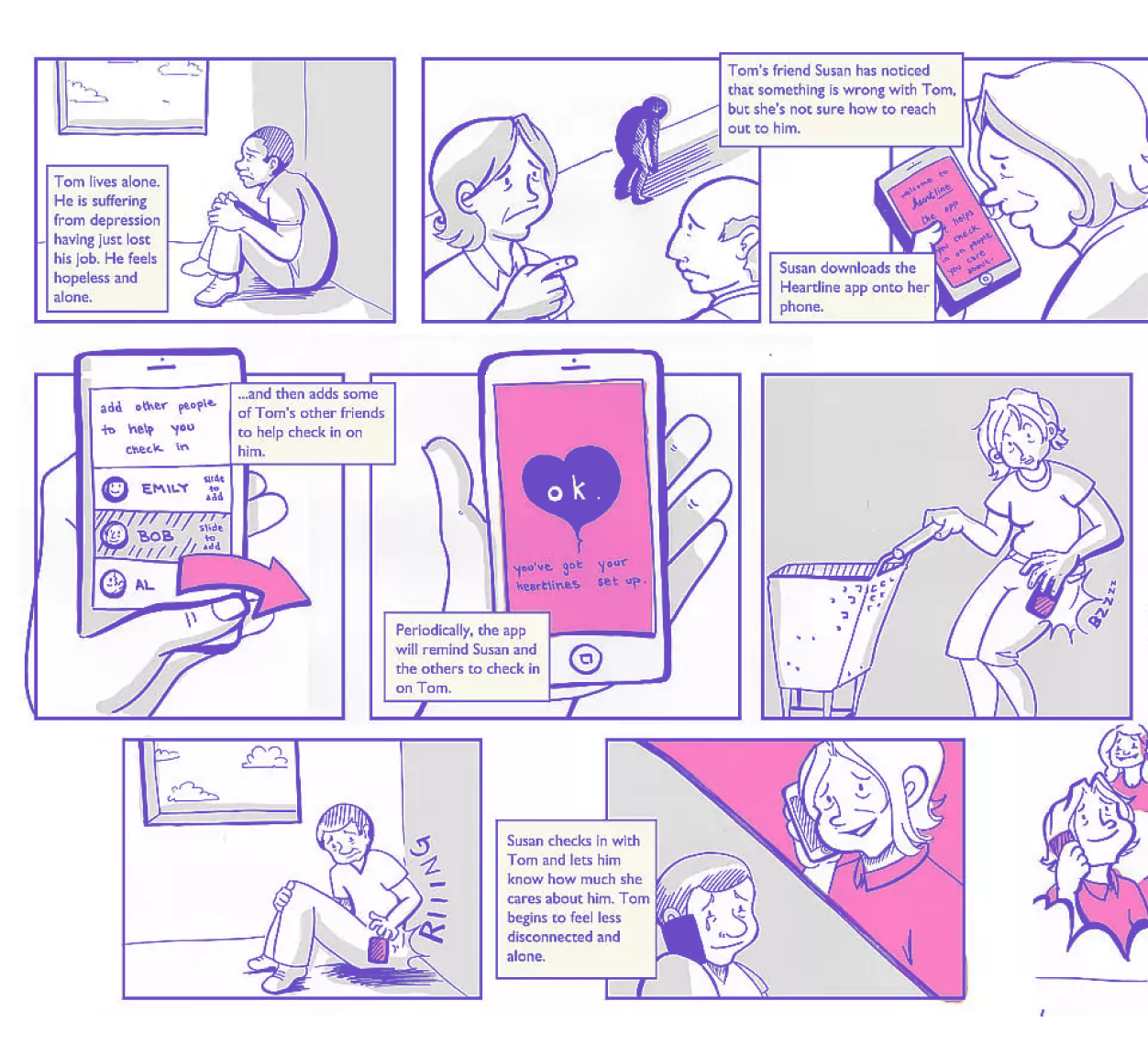
This is a sketch, a kind of storyboard of how the user will interact with the product in the real world, taking into account external factors (his location, emotional state, environmental conditions). This method helps to better understand the context of using the product, highlight key goals and possible problems. The storyboard is a great example of how paper and pencil can be used to quickly and effectively identify product goals and problems.
How to create a storyboard?
- Start over. What precedes the use of the product?
- Take into account all the factors of the user session: lighting, decor, environment, etc.
- Indicate the user's mood at the beginning of his “journey” and at the end of the session.
- Imagine drawing a mini script for a movie, don't focus on the beauty of the drawing.
CJM (Customer Journey Map)
A structured version of the storyboard, when all hypotheses and conditions can be combined into a single picture. CJM shows how the user interacts with the product at certain "junctions". Each such step of interaction should motivate the user to do the next one and remove the "resistance" of the interface.
How to design CJM?
- One CJM is drawn for one person.
- Consider all points of contact and the psycho-emotional state of users at each of these points.
- Pay attention to all channels of customer interaction with the product: online (devices, browsers) and offline (reception departments, pickup points, etc.).
- List all perceived barriers and hypotheses for overcoming them.

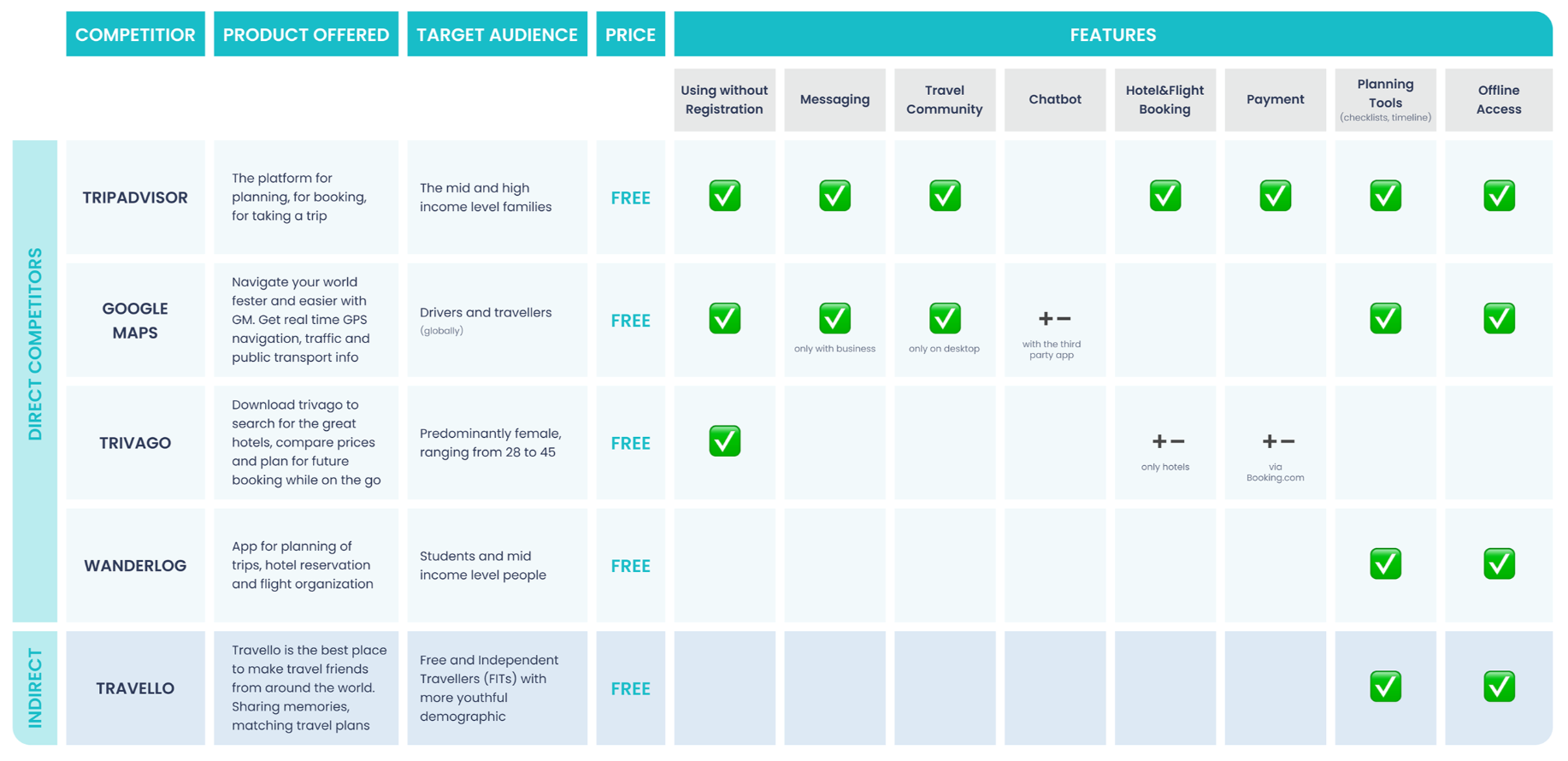
Benchmarking
The object of study in this method are not users, but products. Benchmarking is used to analyze similar products on the market and identify their strengths and weaknesses. Best practices can be adopted. Applicable when the task is to redesign or scale the product.
How to do benchmarking?
- Identify direct and indirect competitors.
- Identify key parameters (product features) for comparison.
- See real user reviews.
- Decide what to measure: at the top level, you can refer to the HEART approach (basic user experience metrics: Happiness, Engagment, Adoption, Retention, Task Success), or more specific indicators (how much time is needed for a particular task, how many sales, sending forms, etc.).
July 11, 2023
